二叉树的最大深度
link:104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
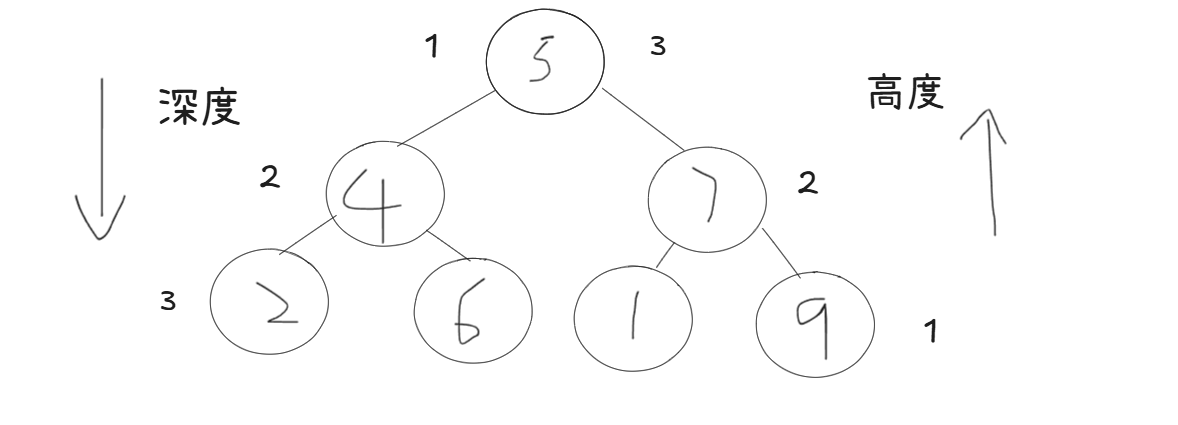
思路分析
高度:后序遍历
深度:前序遍历
但是其实这里我们可以选择后序遍历,根节点的高度就是树的深度.
递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
int height = leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
return height;
}
}
|
二叉树的最小深度
link:111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路分析
和上题的思路基本一致,但是注意不是把最大值改成最小值.
自己画图分析一下有哪些情况,还是之前讲的特殊情况优先考虑.
按照我们上一题的思路,针对左子树只有一个节点,但右子树有至少一层分支的基础上,最小深度就不会是1了.
递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return getHeight(root);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
if(node.left == null && node.right != null) {
return rightHeight + 1;
}
if(node.left != null && node.right == null) {
return leftHeight + 1;
}
return leftHeight>rightHeight?rightHeight+1:leftHeight+1;
}
}
|
完全二叉树节点个数
link:222. 完全二叉树的节点个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路分析
首先想到的是在之前深度的基础上,遍历计数节点,利用完全二叉树的性质,左子树的高度一定是大于等于右子树的高度,所以我们遍历只需要判断左子树就行.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return getNum(root);
}
public int getNum(TreeNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return 0;
}
TreeNode left = node.left;
TreeNode right = node.right;
int leftDepth = 0;
int rightDepth = 0;
while(right != null) {
right = right.right;
leftDepth++;
}
while(left != null) {
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
if(leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (2 >> leftDepth) - 1;
}
int leftnum = getNum(node.left);
int rightnum = getNum(node.right);
int result = leftnum + rightnum + 1;
return result;
}
}
|
优化版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return getNumber(root);
}
public int getNumber(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = getDepth(node.left);
int rightDepth = getDepth(node.right);
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (1 << leftDepth) + getNumber(node.right);
} else {
return (1 << rightDepth) + getNumber(node.left);
}
}
public int getDepth(TreeNode node) {
int depth = 0;
while (node != null) {
depth++;
node = node.left;
}
return depth;
}
}
|


