初探回溯
什么是回溯算法
回溯算法是一种暴力穷举的搜索方式.
回溯和递归是相辅相承的**.(有递归就会有回溯)**
回溯法解决的问题
- 组合问题:N个数里面按一定规则找出k个数的集合.
- 切割问题:一个字符串按一定规则有几种切割方式.
- 子集问题:一个N个数的集合里有多少符合条件的子集.
- 排列问题:N个数按一定规则全排列,有几种排列方式.
- 棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等.
使用回溯算法解决问题的思路
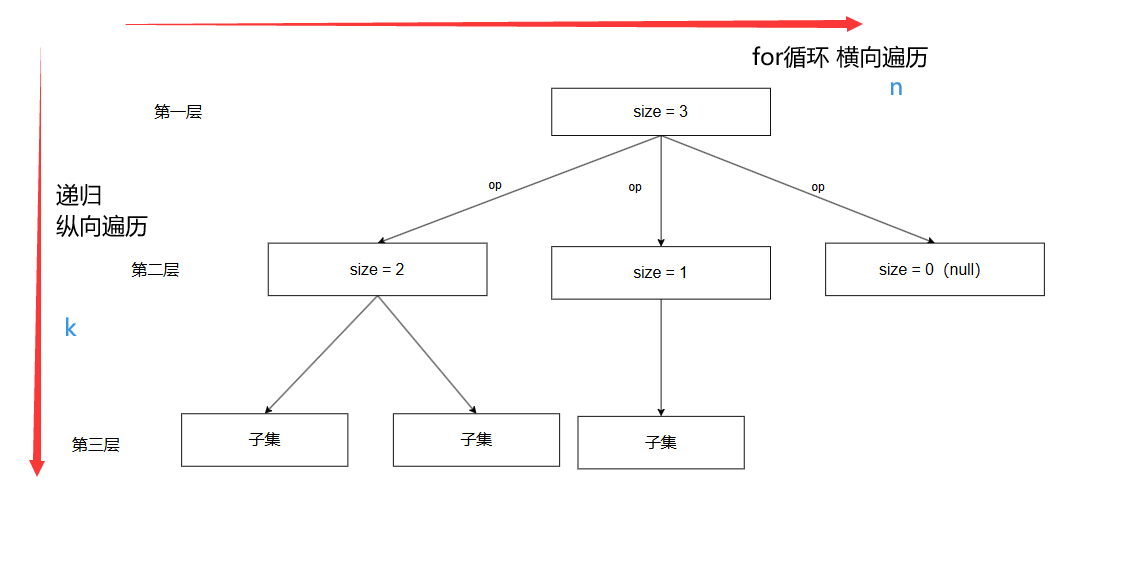
虽然回溯算法暴力效率低下理解起来更为抽象,但好在天无绝人之路,回溯算法的问题都可以用树形结构来进行理解.
关键有以下两点:
1.集合大小->树的宽度
2.递归深度->树的深度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void backtracking(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) {
处理节点;
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
|
组合问题
link:77. 组合 - 力扣(LeetCode)
思路分析
进入到回溯算法的学习!
首先明确是在求组合,组合中的元素是不能重复的.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
backtracking(n,k,1);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(int n, int k,int startIndex)
{
if(path.size() == k)
{
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex;i<=n;i++)
{
path.add(i);
backtracking(n,k,i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
|
优化思路
当我们n=k时,第一层for循环再往后遍历就没有意义了.(因为我们最终要取的数的数量要满足,从第二层开始往后的for循环其实已经自动减少了集合中的子集数量,显然这是不符合预期的)
以下引用代码随想录分析图
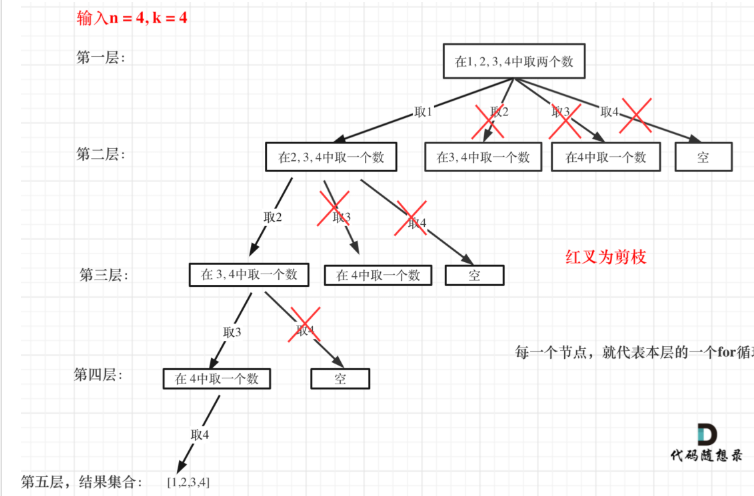
优化部分
1
2
3
| 1.已经选择的元素个数:path.size();
2.还需要的元素个数为: k - path.size();
3.在集合n中至多要从该起始位置 : n - (k - path.size()) + 1,开始遍历
|
优化之后的for循环代码
1
| for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1; i++)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
backtracking(n,k,1);
return result;
}
public void backtracking(int n, int k,int startIndex)
{
if(path.size() == k)
{
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex;i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1;i++)
{
path.add(i);
backtracking(n,k,i+1);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
|


